Montagem e Reparação de computadores. Recuperação de dados. Suporte à sua empresa. Solicite já um orçamento! Contacte: errorsolutions.blogspot@gmail.com
Friday, November 25, 2011
Outlook signatures location
Signatures (.rtf, .txt, .htm)
Windows 7 and Windows Vista
drive:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Signatures
Windows XP
drive:\Documents and Settings\user\Application Data\Microsoft\Signatures
http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/outlook-help/where-does-microsoft-outlook-2010-save-my-information-and-configurations-HP010354943.aspx
Thursday, October 27, 2011
Environment variables / Variáveis de sistema
An environment variable is a dynamic value loaded into the memory that can be used by several processes operating simultaneously. On most operating systems, the location of some libraries or of the main system executables may be different depending on the installation.
It is therefore possible, from a given programme, to refer to a location based on the environment variables that define these data.
In Windows, the environment variables are placed between the "%" character. Thus to display the value of an environment variable, simply type following type of command:
echo %NAME_OF_THE_VARIABLE%Here is a non-exhaustive list of the main environment variables on Windows systems:
Environment variable Description
%APPDATA% Returns an access path to the default directory containing the user programmes (by default: C:\Program Files\.
%CMDCMDLINE% Returns the exact command used to access the command interpreter (cmd.exe).
%COMPUTERNAME% Returns the name attributed to the computer.
%DATE% Returns the day's date.
%ERRORLEVEL% Contains the error code of the latest command used.
%HOMEDRIVE% Contains the letter of the drive on which the current user's directory is located.
%HOMEDRIVE% Contains the letter of the drive on which the current user's directory is located.
%HOMEPATH% Contains the full access path to the current user's directory.
%NUMBER_OF_PROCESSOR% Contains the number of processors present on the system.
%OS% Contains a chain of characters describing the operating system installed. Note that Windows 2000 is identified as WINDOWS_NT.
%PATH% Specifies the access path to the system's main executables.
%PATHEXT% Describes the extensions that the system considers to be executable.
%PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE% Describes the architecture of the processor (x86 for Intel machines, IA64 for RISC architectures).
%RANDOM% Returns an integer between 0 and 32167 chosen at random by the system.
%SYSTEMDRIVE% Contains the letter of the drive on which the system is located (generally C:).
%SYSTEMROOT% Contains the access path to the system's root directory.
%TEMP% Contains the temporary directory access path for the applications.
%TMP% Contains the temporary directory access path for the applications.
%TIME% Returns the day's date.
%USERDOMAIN% Contains the domain to which the current account belongs.
%USERNAME% Contains the user name corresponding to the current account.
%USERPROFILE% Contains the location of the current account user profile.
%WINDIR% Contains the access path to the system's directory (generally C:\WINDOWS or C:\WINNT).
In Windows, the set command allows creation, modification and display of the environment variables. However, changes are made only in the session in progress.
To display a variable, the following command is used:
set VariableName To create a variable, the following command is used:
set VariableName=valueTo delete a variable, the following command is used:
set VariableName=It is possible to use any character as a value, including spaces. However, to be able to use special characters (<, >, , & or ^), simply place the (^) escape character in front of them or quotation marks around them, which will then be part of the value since all characters following the = sign are taken into account. For example, to define "black&white" as the value:
set colour=black^&white
or
set varname="new&name"
Thursday, July 28, 2011
Windows 7 ShortKeys and Shortcuts
Window Management Shortcuts
You can also interact with windows by dragging them with the mouse:
- Drag window to the top: Maximize
- Drag window left/right: Dock the window to fill half of the screen.
- Shake window back/forth: Minimize everything but the current window.
- Double-Click Top Window Border (edge): Maximize window vertically.
Taskbar Shortcuts
- Win+number (1-9): Starts the application pinned to the taskbar in that position, or switches to that program.
- Shift+Win+number (1-9): Starts a new instance of the application pinned to the taskbar in that position.
- Ctrl+Win+number (1-9): Cycles through open windows for the application pinned to the taskbar in that position.
- Alt+Win+number (1-9): Opens the Jump List for the application pinned to the taskbar.
- Win+T: Focus and scroll through items on the taskbar.
- Win+B: Focuses the System Tray icons
In addition, you can interact with the taskbar using your mouse and a modifier key:
- Shift+Click on a taskbar button: Open a program or quickly open another instance of a program.
- Ctrl+Shift+Click on a taskbar button: Open a program as an administrator.
- Shift+Right-click on a taskbar button: Show the window menu for the program (like XP does).
- Shift+Right-click on a grouped taskbar button: Show the window menu for the group.
- Ctrl+Click on a grouped taskbar button: Cycle through the windows of the group.
More Useful Hotkeys You Should Know
- Ctrl+Shift+N: Creates a new folder in Windows Explorer.
- Alt+Up: Goes up a folder level in Windows Explorer.
- Alt+P: Toggles the preview pane in Windows Explorer.
- Shift+Right-Click on a file: Adds Copy as Path, which copies the path of a file to the clipboard.
- Shift+Right-Click on a file: Adds extra hidden items to the Send To menu.
- Shift+Right-Click on a folder: Adds Command Prompt Here, which lets you easily open a command prompt in that folder.
- Win+P: Adjust presentation settings for your display.
- Win+(+/-): Zoom in/out.
- Win+G: Cycle between the Windows Gadgets on your screen.
Others:
Win+UP Arrow :- Maximize the current window
Win+Down Arrow :- If the current window is maximized, restore it; if the current window is restored, minimize it
Win+Left Arrow :- Dock the current window to the left half of the screen
Win+Right Arrrow :- Dock the current window to the right half of the screen
Win+Home :- Minimize all but the current window
Win+P :- Open the projection menu (generally used for laptops connected to projectors)
Alt+F4 :- Close the active window
Alt+Tab :- Switch to previous active window
Alt+Esc :- Cycle through all open windows
Win+Tab :- Flip 3D
Ctrl+Win+Tab :- Persistent Flip 3D
Win+T :- Cycle through applications on taskbar (showing its live preview)
Win+M :- Minimize all open windows
Win+Shift+M :- Undo all window minimization
Win+D :- Toggle showing the desktop
Win+Up Arrow :- Maximize the current window
Win+Down Arrow :- If the current window is maximized, restore it; if the current window is restored, minimize it
Win+Left Arrow :- Dock the current window to the left half of the screen
Win+Right Arrow :- Dock the current window to the right half of the screen
Win+Home :- Minimize all but the current window
How to configure gmail account on Windows Live Mail
Access a Gmail Account in Windows Live Mail Using IMAP
To set up Gmail as an IMAP account in Windows Live Mail:
•Make sure IMAP access is enabled in Gmail.
•Select Go Mail from the menu in Windows Live Mail.
•Hold down the Alt key if you cannot see the menu bar.
•Click Add an e-mail account at the bottom of the list.
•Type your Gmail address under E-mail address:.
•Type your Gmail password under Password:.
•Enter your name under Display Name:.
•Make sure Automatically determine my login ID is checked. (You can verify it is working correctly if the local part, i.e. what comes before the @, in your Gmail address appears under Login ID:.)
•Type your Gmail password under Password:.
•Make sure Manually configure server settings for e-mail account. is checked.
•Click Next.
•Make sure IMAP is selected under My incoming mail server is a ___ server.
•Enter "imap.gmail.com" under Incoming server:.
•Make sure This server requires a secure connection (SSL) is checked under Incoming Server Information.
•Type "smtp.gmail.com" under Outgoing server:.
•Make sure This server requires a secure connection (SSL) is also checked under Outgoing Server Information.
•Also check My outgoing server requires authentication.
•Type "465" for Port: under Outgoing Server Information.
•Click Next.
•Now click Finish.
•Click OK.
•Select Tools Accounts... from the menu.
•Highlight the Gmail account in the list.
•Click Properties.
•Go to the IMAP tab.
•Enter "[Gmail]#Sent Mail" (not including the quotation marks) under Sent Items path:.
•Type "[Gmail]#Drafts" under Drafts path:.
•Type "[Gmail]#Trash" under Deleted Items path:.
•Enter "[Gmail]#Spam" under Junk path:.
•Click OK.
•Click Close.
•Close Windows Live Mail.
•Open Gmail in your browser.
•Select Settings in the top right navigation bar.
•Go to Labels.
•Click Remove followed by OK for the "[Imap]/Deleted Items", "[Imap]/Drafts", "Junk E-mail" and "Sent Items" labels.
•Open your Windows Live Mail folder in Windows.
•Go to the Gmail (user name) sub-folder.
•Open Notepad.
•Drag and drop the account{***}.oeaccount (where "***" represents a long random string) file from the imap.gmail.com onto Notepad to open it.
•Look for the '#' in "[Gmail]#Sent Items", "[Gmail]#Drafts", "[Gmail]#Trash" and "[Gmail]#Spam" and replace it with '/' (always excluding the quotation marks).
•After editing, "[Gmail]#Sent Items" should read "[Gmail]/Sent Items", for example.
•Close Notepad saving the file.
•Start Windows Live Mail.
•Select Tools IMAP Folders... from the menu.
•Choose the Gmail account under Account(s):.
•Click Reset List.
•Now click OK.
•Choose the desired synchronization settings for your folders:
•Click on each folder in succession with the right mouse button in the folder list and choose the desired setting under Synchronization settings in the menu that pops up.
•Do not enable synchronization for [Gmail]/All Mail unless you want Windows Live Mail to download all messages in your Gmail account.
•You can safely turn off synchronization for the Spam and Trash folders.
•Select Tools Options... from the menu.
•Go to the Advanced tab.
•Make sure Use the 'Deleted Items' folder with IMAP accounts is checked under IMAP.
•Click OK.
Access a Gmail Account in Windows Live Mail Using POP
To set up access to a Gmail account in Windows Live Mail:
•Make sure POP access is turned on for your Gmail account.
•Go to Mail under Shortcuts in Windows Live Mail.
•Click Add an e-mail account at the bottom of the list.
•Type your Gmail address under E-mail address:.
•Type your Gmail password under Password:.
•Enter your name under Display Name:.
•Make sure Manually configure server settings for e-mail account. is not checked.
•Click Next.
•Click Finish.
•Click Send/receive in the Windows Live Mail toolbar.
That's it. By now, a Gmail account should have appeared in the folder pane, and if you had any mail waiting in Gmail, it is now in its Inbox.
Monday, July 4, 2011
Change Office 2007 serial Key
1.Click Start -> Run
2.Type regedit in the box and click OK
3.Navigate to the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \Software\Microsoft\Office\12.0\Registration
Within Registration, there is subkey that may resemble the following:
{30120000-0011-0000-0000-0000000FF1CE}
4.Under Registration, you might find several subkeys that contain a combination of alphanumeric characters. Each key is specific to a program installed on your computer.
Open each subkey to view and identify the Office product version by the ProductName registry entry in the right pane. For example:
ProductName=Microsoft Office Professional Plus 2007
5.Once you have located the subkey that contains the Office product you wish to change the license key for, delete the following registry entries by right clicking on the registry entry in the subkey, click Delete, and select Yes:
DigitalProductID
ProductID
6.Close regedit
7.Start Microsoft Word, Excel, Outlook or another Office application. Office 2007 should now prompt you to enter a new 25 character product key
8.Enter a valid product key, and click OK
9.If prompted to choose your preferred type of Microsoft Office 2007 installation, select Install Now
10.Microsoft Office 2007 should now be updated with your new CD key
Tuesday, May 31, 2011
Create USB with Multiboot
It is a Windows based application that can be used to create a Live Multiboot USB or even a Multiboot ISO file that can then be burnt to a CD/DVD.
XBOOT supports many Linux Distributions and Utilities, and allows you to use your choice of a Grub or Syslinux bootloader.
Also included is a built in QEMU emulator (enabling you to boot an ISO from within Windows).
XBOOT – Multiboot ISO/USB Creator
http://sites.google.com/site/shamurxboot/download
Usage Example: Creating a Live Multiboot USB with XBOOT:
1.Download, extract and run the latest version of XBOOT
2.(1) Drag and drop some ISOs into the XBOOT window (2) Select Create USB
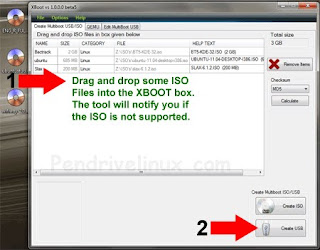
XBOOT – Multiboot ISO USB Creator (Windows)
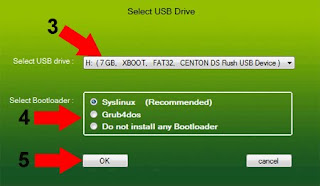
3.(3) Select your USB Drive from the Droplist (4) Select a Bootloader to use (5) Click OK to begin creation
A copy notification window appears to keep you informed of the progress. Once the process is complete, you should have a Bootable Multiboot USB Flash Drive with your ISO selections installed.

Monday, May 23, 2011
SQL Best Practices - HDD Architecture
C:\ OS
E:\ SQL Binaries
R:\ TempDB (1 file per processor, equi-sized)
S:\ Data
T:\ Log
and
C:\ RAID-1
E:\ RAID-5
R:\ RAID-1 or RAID-10
S:\ RAID-5
T:\ RAID-1 or RAID-10
Working with tempdb in SQL Server 2005
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc966545.aspx
Storage Top 10 Best Practices
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc966534.aspx
Disk Partition Alignment Best Practices for SQL Server
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd758814(v=sql.100).aspx